Java Interview Question and Answers
Java Interview Question and Answers
1-
What is Java?
A-
Java is a
high level programming language originally developed by Sun Microsystems and
released in 1995.
2-
Why called Java
is platform independent language?
A-
Java runs on
a variety of platforms, such as Windows, Mac OS, and the various versions of
UNIX/LINUX (like
HP-Unix, Sun Solaris, Redhat Linux, Ubuntu, CentOS, etc.). So that is why called java is platform independent
language.
3-
List any five
features of Java?
A-
Some features include Object Oriented, Platform
Independent, Robust, Interpreted, Multi-threaded.
4-
List two Java
IDE’s?
A-
Netbeans, Eclipse, etc.
5-
What is JVM (Java
Virtual Machine)?
A-
Java Virtual
Machine is a process of virtual machine that can execute Java bytecode. Each
Java source file is compiled into a bytecode file, which is executed by the
JVM.
6-
What is JDK (Java
Development Tool Kit)?
A-
The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is basically the Java
Virtual Machine (JVM) where your Java programs are being executed.
7-
What is JRE (Java
Run-Time Environment)?
A-
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is the full featured
Software Development Kit for Java, including the JRE, the compilers and tools
(like JavaDoc, and Java Debugger), in order for a user to develop, compile and
execute Java applications.
8-
What are the
Data Types of Java?
A-
The eight primitive data types supported by the Java
programming language are: • byte • short • int • long • float • double •
boolean • char
9-
What is
Object?
A-
A Java object is a combination of data
and procedures working on the available data. An object has a state and
behavior. The state of an object is stored in fields (variables), while methods
(functions) display the object's behavior. Objects are created from templates
known as classes. In Java, an object is created using the keyword
"new".
10-
What is
class?
A-
A class is a
blue print from which individual objects are created. A class can contain
fields and methods to describe the behavior of an object.
11-
What kind of
variables a class can consist of?
A-
A class
consists of Local variable, instance variable and class variables.
12-
What is
Method Overriding and Overloading in java?
A-
Method overloading in Java occurs when two or more
methods in the same class have the exact same name, but different parameters.
On the other hand, method overriding is
defined as the case when a child class redefines the same method as a parent
class. Overridden methods must have the same name, argument list, and return
type.
13-
What is OOP’s?
A-
Object-Oriented Programming is a
paradigm that provides many concepts such as inheritance, data binding, polymorphism, etc. The
main aim of object-oriented programming is to implement real-world entities for
example abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism .
14-
Does Java
support multiple inheritances?
A-
No, Java does not support multiple inheritance. Each class
is able to extend only on one class, but is able to implement more than one
interfaces.
15-
What is the
default value of datatypes in Java?
A-
Default value
of Byte datatype is 0.
B-
Default value
of Float datatype is 0.0f.
C-
Default value
of Double datatype is 0.0d.
16-
What do you mean by Access Modifier?
A-
Java provides access modifiers to set access levels for
classes, variables, methods and constructors.
17-
Variables used in a switch statement can be used with
which datatypes?
A-
Variables used in a switch statement can only be a byte,
short, int, or char.
18-
When parseInt method can be used?
A-
This method is used to get the primitive data type of a
certain String.
19-
Which package is used for pattern matching with regular
expressions?
A-
Java.util.regex package is used for this purpose.
20-
Java.util.regex consists of which classes?
A-
Java.util.regex consists of three classes − Pattern class,
Matcher class and PatternSyntaxException class.
21-
Which are the two subclasses under Exception class?
A-
The Exception class has two main subclasses: IOException
class and RuntimeException Class.
22-
When throws keyword is used?
A-
If a method does not handle a checked exception, the
method must declare it using the throws keyword. The throws keyword appears at
the end of a method's signature.
23-
When throw keyword is used?
A-
An exception can be thrown, either a newly instantiated
one or an exception that you just caught, by using throw keyword.
24-
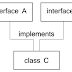
What is an Interface?
A-
An interface is a collection of abstract methods. A class
implements an interface, thereby inheriting the abstract methods of the
interface.
25-
What exactly is a .class file? A. It's a
binary file (sequence of 0s and 1s).
A-
If you are using Unix or OS X, you can examine
its contents by typing od -x HelloWorld.class at the command prompt. This
displays the results in hexadecimal (base 16). In deference to Java's name, the
first word of every .class file is cafe.
26-
Why is the type for real numbers called
double?
A- Historically, the type for
floating point numbers was float, but they had limited accuracy. The type double
was introduced as a floating point type with twice as much accuracy.
27-
Why doesn't the statement if (a <= b <=
c) work?
A-
The <= operator cannot be chained. Instead,
use if (a <= b && b <= c).
28-
What are pass by reference and pass by value?
A-
When an object is passed by value, this
means that a copy of the object is passed. Thus, even if changes are made to
that object, it doesn’t affect the original value. When an object is passed by
reference, this means that the actual object is not passed, rather a reference
of the object is passed. Thus, any changes made by the external method, are
also reflected in all places.
29-
What is the difference between processes and
threads?
A-
A process is an execution of a program, while a
Thread is a single execution sequence within a process. A process can contain
multiple threads. A Thread is sometimes called a lightweight process.
30-
What is the difference between a synchronized
method and a synchronized block?
A-
In Java programming, each object has a lock. A
thread can acquire the lock for an object by using the synchronized keyword.
The synchronized keyword can be applied in a method level or block level of
code .
Thanking you !!
Java Interview Question and Answers
![Java Interview Question and Answers]() Reviewed by Unknown
on
October 06, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Unknown
on
October 06, 2018
Rating:





No comments: